基本知识
虽然回溯法很难,很不好理解,但是回溯法并不是什么高效的算法 。
因为回溯的本质是穷举,穷举所有可能,然后选出我们想要的答案 ,如果想让回溯法高效一些,可以加一些剪枝的操作,但也改不了回溯法就是穷举的本质。
回溯法问题总结
组合问题 :N个数里面按一定规则找出k个数的集合切割问题 :一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式子集问题 :一个N个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集排列问题 :N个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式棋盘问题 :N皇后,解数独等等
组合无序,排序有序
回溯法模板
回溯法解决的问题都可以抽象为树形结构 ,集合的大小就构成了树的宽度,递归的深度,都构成的树的深度 。递归就要有终止条件,所以必然是一棵高度有限的树(N叉树)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void backtracking (参数) if (终止条件) {return ;for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {
⭐ 回溯三步:
回溯函数模板返回值(一般是void)以及参数
回溯函数终止条件
一般来说搜到 叶子节点 了,也就找到了满足条件的一条答案,把这个答案存放起来,并结束本层递归。
所以回溯函数终止条件伪代码如下:
1 2 3 4 if (终止条件) {return ;
回溯搜索的遍历过程
回溯法一般是在集合中递归搜索,集合的大小构成了树的宽度,递归的深度构成的树的深度。
for循环可以理解是横向遍历,backtracking(递归)就是纵向遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {
不能忘记回溯撤销
组合问题
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。
思路
叶子节点:每个组合的第k个数,即子组合长度为k
每个节点就是往集合里加数
横向遍历: 剪枝 [起始,剩下的数](不剪枝就是<=n)
关键:如何避免重复?——每次递归的时候取[]中下一个数
起始:i=t,递归时变成i+1
剩下的数:= n - 集合中还差的数的个数 +1 (保证还有足够的数可以被遍历)
集合中还差的数的个数 = (k-comb.size())
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();public LinkedList<Integer> comb = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {1 );return res;public void backtracking (int n, int k, int t) if (comb.size() == k) {new ArrayList<>(comb));return ;for (int i = t; i <= n - (k - comb.size()) + 1 ; i++) {1 );
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
思路: 参考上面的模板,一下就写对啦!
终止条件:
size=k且sum=n,符合条件,res.add
size=k但sum!=n,结束
按从小到大遍历的话,如果sum>n,结束
横向遍历 [1,9]–》[t,9-(k-size)+1], t=i+1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public int sum = 0 ;public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {1 );return res;public void sumComb3 (int k, int n, int startIndex) int sz = path.size();if (sz == k && sum == n) {new ArrayList<>(path));return ;if (sum > n || (sz == k && sum != n)) {return ;for (int i = startIndex; i <= 9 - (k - sz) + 1 ; i++) {1 );
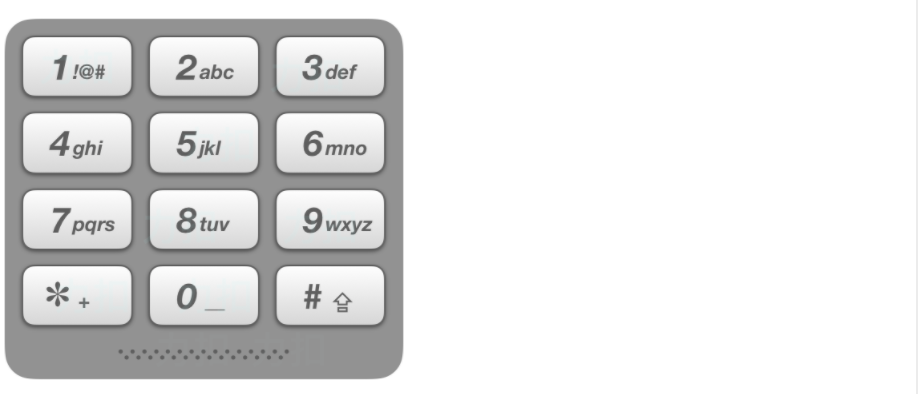
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:digits = "23"
示例 2:
示例 3:
1 2 输入:digits = "2"
思路:
首先要思考清楚题意,每个数字相当于一个字母的集合(用字符串数组表示出来)
每个集合里都要取一个数,构成最终的集合
因为是集合(答案可以按任意顺序返回),所以按顺序来就行
每层迭代是每个数字内部的集合遍历
每层递归是下一个“数字”代表的集合
终止条件是没有数字了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution public final String[] digitStr = {"" ,"" ,"abc" , "def" , "ghi" , "jkl" , "mno" , "pqrs" , "tuv" , "wxyz" , public List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0 ) {return res;new StringBuilder();0 , temp);return res;public void backtracking (String digits, int i, StringBuilder temp) if (i == digits.length()) {return ;int digit = digits.charAt(i) - '0' ;for (int k = 0 ; k < digitStr[digit].length(); k++) {1 , temp);1 );
关键问题和错误:
涉及字符串拼接,选用StringBuilder
转换成String: .toString()
添加:.append(ch)
删除最后一个:deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1);
字符串的第K个字母: .charAt(k)
⭐ digit的第k位,转换为数字:int digit = digits.charAt(i) - '0';
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
思路: 先排序
这题在[数组](/augu1sto/0d8a87a8eab4/#39-组合总和)里写过,不赘述
终止条件
sum==target,加进结果列表,返回
sum>target,再往后遍历也更大,直接返回
虽然我也不是很懂,这个判断条件写进循环里,效率会高很多。。
遍历,因为排序过了,每次从下一个值开始遍历 ❌
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public int sum = 0 ;public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int [] candidates, int target) {0 );return res;public void sumComb (int [] nums, int target, int startIndex) if (sum==target){new ArrayList<>(path));return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length&&(sum+nums[i]<=target); i++) {
给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
注意: 解集不能包含重复的组合。
思路
和上一题差不多,遍历的时候从下一个数开始就行了
但是要去重,也就是说for循环的时候如果下一个数和当前数相等,跳过continue就行了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public int sum = 0 ;public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int [] candidates, int target) {0 );return res;public void sumComb2 (int [] nums, int target, int startIndex) if (sum==target){new ArrayList<>(path));return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length&&(sum+nums[i]<=target); i++) {if (i>startIndex&&nums[i]==nums[i-1 ]) {continue ;1 );
切割问题
从startIndex循环,确定长度
切割条件的判断,不满足条件就continue
给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:s = "aab"
思路
两个关键问题:
切割问题,有不同的切割方式
判断回文
终止条件:
逻辑:
用startIndex表示切割线
循环i表示切割长度
如果是回文就记录到path中
优化:记忆化搜索
用f[i][j] = 0 表示未搜索,1 表示是回文串,-1 表示不是回文串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution new ArrayList<>();new LinkedList<>();int [][] f;public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {new int [s.length()][s.length()];0 );return res;public void backtracking (String s, int startIndex) if (startIndex>=s.length()) {new ArrayList<>(path));return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {1 );if (isPal(s,startIndex,i)==-1 ) {continue ;1 );public int isPal (String s, int i, int j) if (f[i][j] != 0 ) {return f[i][j];if (i >= j) {1 ;else if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {1 , j - 1 );else {1 ;return f[i][j];
用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能的有效 IP 地址 (不能有前缀0),这些地址可以通过在 s 中插入 '.' 来形成。你 不能 重新排序或删除 s 中的任何数字。你可以按 任何 顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:s = "25525511135"
思路
除了index,还要用cnt来记录是第几次切割,根据剩下的位数len-startIndex剪枝
第1次前:4~12位
第2次前:3~9位
第3次前:2~6位
第4次前:1~3位
总结:(4-cnt+1) ~ 3*(4-cnt+1)位
每次切割最多3位
如果首字母==0,只能切1位
有效:转换为十位数在0-255之间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution public List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();public String[] arr = new String[4 ];public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) 0 , 1 );return res;public void cutting (String s, int startIndex, int cnt) if (startIndex==s.length()&&cnt==4 +1 ) {"." , arr));return ;if ((s.length()-startIndex<4 -cnt+1 )||(s.length()-startIndex>3 *(4 -cnt+1 ))) {return ;if (s.charAt(startIndex)=='0' ){1 ]="0" ;1 , cnt+1 );return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length()&&i < startIndex+3 ; i++) {1 );if (Integer.parseInt(st)<0 ||Integer.parseInt(st)>255 ) {continue ;1 ]=st;1 , cnt+1 );
数据结构选型
字符串数组长度固定+要用特定字符拼接:用String[]
注意细节!!
子集问题
组合问题和分割问题都是收集树的叶子节点,而子集问题是找树的所有节点
遍历时记录所有节点(写在递归开头)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int [] nums) {0 );return res;public void backtracking (int [] nums, int startIndex) new ArrayList<>(path));if (startIndex == nums.length) {return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {1 );
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中可能包含重复元素,请你返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。返回的解集中,子集可以按 任意顺序 排列。
思路 先排序,循环遍历时跳过和上一个一样的数(参考组合)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int [] nums) {0 );return res;public void backtracking (int [] nums, int startIndex) new ArrayList<>(path));if (startIndex == nums.length) {return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {if (i > startIndex && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) { continue ;1 );
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出并返回所有该数组中不同的递增子序列,递增子序列中 至少有两个元素 。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
数组中可能含有重复元素,如出现两个整数相等,也可以视作递增序列的一种特殊情况。
思路: 套子集模板
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int [] nums) {0 );return res;public void backtracking (int [] nums, int startIndex) if (path.size() >= 2 ) {new ArrayList<>(path));if (startIndex == nums.length) {return ;int [] visited = new int [201 ]; for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {if (100 ] == 1 )continue ;100 ] = 1 ;1 );
排列问题
给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
思路
不需要startIndex,但是要去重,记录哪些元素用过了(记得回溯)
和上一题不同,这次直接申请nums长度的used数组就行了
used[i]表示num[i]是否出现过
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public boolean [] used;public List<List<Integer>> permute(int [] nums) {new boolean [nums.length];return res;public void backtracking (int [] nums) if (path.size() == nums.length) {new ArrayList<>(path));return ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (used[i]) {continue ;true ;false ;
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序
思路
先排序,遍历时比较节点的值是否与上一个相同(line22),记得查看是否被访问过
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();public LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public boolean [] used;public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int [] nums) {new boolean [nums.length];return res;public void backtracking (int [] nums) if (path.size() == nums.length) {new ArrayList<>(path));return ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && used[i - 1 ] == false ) {continue ;if (used[i] == true ) {continue ;true ;1 );false ;
如果改成 used[i - 1] == true, 也是正确的! ,去重代码如下:
1 2 3 if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && used[i - 1 ] == true ) {continue ;
如果要对树层中前一位去重,就用used[i - 1] == false,如果要对树枝前一位去重用used[i - 1] == true。
对于排列问题,树层上去重和树枝上去重,都是可以的,但是树层上去重效率更高!
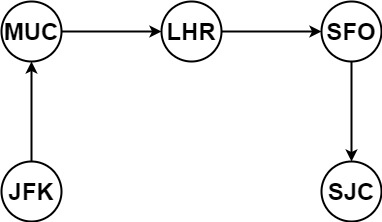
给你一份航线列表 tickets ,其中 tickets[i] = [fromi, toi] 表示飞机出发和降落的机场地点。请你对该行程进行重新规划排序。
所有这些机票都属于一个从 JFK(肯尼迪国际机场)出发的先生,所以该行程必须从 JFK 开始。如果存在多种有效的行程,请你按字典排序返回最小的行程组合。
例如,行程 ["JFK", "LGA"] 与 ["JFK", "LGB"] 相比就更小,排序更靠前。
假定所有机票至少存在一种合理的行程。且所有的机票 必须都用一次 且 只能用一次。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:tickets = [["MUC" ,"LHR" ],["JFK" ,"MUC" ],["SFO" ,"SJC" ],["LHR" ,"SFO" ]]"JFK" ,"MUC" ,"LHR" ,"SFO" ,"SJC" ]
思路
建立{起点:{终点}}的映射集合:用Map
其中{终点}要以字典序排序,所以选用有自然优先级的容器TreeMap(回溯)/PriorityQueue(官方题解dfs)
下面是回溯法的步骤
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution private Deque<String> res;private Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> map;public List<String> findItinerary (List<List<String>> tickets) new HashMap<String, Map<String, Integer>>();new LinkedList<>();for (List<String> t : tickets) {if (map.containsKey(t.get(0 ))) {0 ));1 ), temp.getOrDefault(t.get(1 ), 0 ) + 1 );else {new TreeMap<>(); 1 ), 1 );0 ), temp);"JFK" );return new ArrayList<>(res);private boolean backTracking (int ticketNum) if (res.size() == ticketNum + 1 ) {return true ;if (map.containsKey(last)) { for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> target : map.get(last).entrySet()) {int count = target.getValue();if (count > 0 ) {1 );if (backTracking(ticketNum)) return true ;return false ;
方法二: DFS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution new HashMap<String, PriorityQueue<String>>();new LinkedList<String>();public List<String> findItinerary (List<List<String>> tickets) for (List<String> ticket : tickets) {0 ), dst = ticket.get(1 );if (!map.containsKey(src)) {new PriorityQueue<String>());"JFK" );return itinerary;public void dfs (String curr) while (map.containsKey(curr) && map.get(curr).size() > 0 ) {
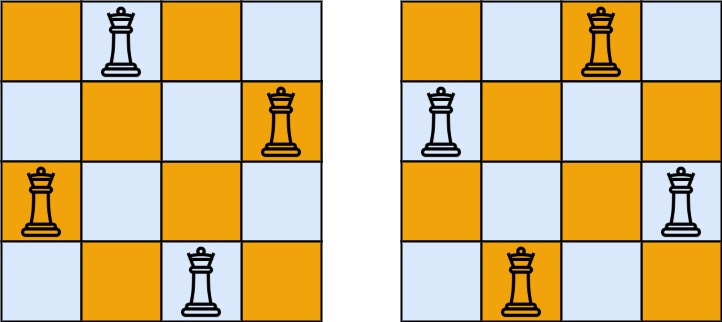
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:n = 4
示例 2:
思路:
皇后们的约束条件:
不能同行
不能同列
不能同斜线
用4个数组记录该行、列、左斜/右斜有没有被访问过
因为在单层搜索的过程中,每一层递归,只会选for循环(也就是同一行)里的一个元素,所以不用去重了。
对于cb[row][col]
used_c[col]==1,说明被访问过
左斜线可以用 used_l[row+col]==1,表示访问过
右斜线可以用 used_r[n-1-row+col]==1,表示访问过
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution new ArrayList<>();int [] used_c;int [] used_l;int [] used_r;public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {new String[n];new int [n];new int [2 *n-1 ];new int [2 *n-1 ];0 );return res;public void helper (int n, int row) if (row==n) {new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(path)));return ;char [] st = new char [n];'.' );for (int col = 0 ; col < n; col++) {if (used_c[col]==1 ||used_l[row+col]==1 ||used_r[n-1 -row+col]==1 ) {continue ;'Q' ;1 ;1 ;1 -row+col]=1 ;new String(st);1 ); '.' ;0 ;0 ;1 -row+col]=0 ;
注意:
使用的类型以及类型转化
引用类型要new一个再传参
String没有办法随便更改某一位的值,故这里用char[]再进行转换
说不定有其他更方便的数据结构
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
数独的解法需 遵循如下规则 :
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
数独部分空格内已填入了数字,空白格用 '.' 表示。
思路
对每一个数看三个地方有没有重复解:
行 new row[9]
列 new col[9]
块 new block[9]
用行r和列c来表示第b块 b=3*(r/3)+c/3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 class Solution int [][] row = new int [9 ][9 ];int [][] col = new int [9 ][9 ];int [][] block = new int [9 ][9 ];public void solveSudoku (char [][] board) for (int i = 0 ; i < board.length; i++) {for (int j = 0 ; j < board.length; j++) {if (board[i][j]!='.' ) {int num = board[i][j]-'0' ;1 ][i] = 1 ;1 ][j] = 1 ;1 ][3 *(i/3 )+j/3 ] = 1 ;public boolean solve (char [][] board) for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++) {for (int j = 0 ; j < 9 ; j++) {if (board[i][j]!='.' ) {continue ;for (int num = 1 ; num <= 9 ; num++) {if (!checkValid(board, i, j, num)) {continue ;char )(num+'0' );1 ][i] = 1 ;1 ][j] = 1 ;1 ][3 *(i/3 )+j/3 ] = 1 ;if (solve(board)) {return true ;'.' ;1 ][i] = 0 ;1 ][j] = 0 ;1 ][3 *(i/3 )+j/3 ] = 0 ; return false ;return true ;public boolean checkValid (char [][] board, int i, int j, int num) if (row[num-1 ][i]==1 ||col[num-1 ][j]==1 ||block[num-1 ][3 *(i/3 )+j/3 ]==1 ) {return false ;return true ;
我的老天爷!!!把除号和模号搞错了!!纠结好久。。救命
runtime beats 53.4 %
或许用其他方法更快?(位运算,见官方题解)